Properly selected lighting in an office space not only creates coziness and comfortable atmosphere in a team, but also contributes to the normal performance of employees during the working day, and aims them at solving production problems. Therefore, it is very important to correctly calculate the number of lamps and their power for a particular room. The most common design solution When decorating the ceiling in offices, the Armstrong ceiling is used. To make the most accurate calculation of the number of Armstrong lamps, it is necessary to take into account the following characteristics of the room:
Calculating the number of Armstrong lamps will be most accurate if you use a universal formula to determine the amount of light, which takes into account the light reflectance of all surfaces in an office space: ceiling, walls, floor, work surfaces. It is necessary to know exactly the dimensions of the room, its area, ceiling height and the distance from the intended light source to the working surface.
We will perform calculations using simple formulas using a specific algorithm. To work, we will need tables indicating standard reflection coefficients various surfaces. These are public reference values. Also, using the tables, it is easy to determine the required illumination levels for various work surfaces and the characteristics of various lamps.
Q = (Z * S) / (Y * k *Pl * V), Where
Z is the required level of illumination of the desktop or surface,
S is the area of the room,
Y is the productivity coefficient of the lighting system,
k is the number of lamps in one lighting system,
Pl is the intensity of the light flux emanating from one lamp,
V - wear coefficient. Takes into account the decrease in lighting brightness over time due to contamination of the lamp or surfaces in the room.
This method allows you to calculate Armstrong ceiling lamps, but the calculations are labor-intensive and not always accurate. In order to accurately calculate the amount of illumination in an office space, it is important to take into account as correctly as possible many factors, the exact area of the office, its architecture and design, the texture of the floor and walls, the number and arrangement of furniture, the intensity of the natural light flux in daytime and the amount of light emitted by other sources, the dustiness of the room, and so on. It is also important to consider the purpose of the office premises and what work is carried out in them.
In a traditional standard situation, it is believed that one Armstrong lamp is capable of providing the necessary illumination over a room area of five square meters.
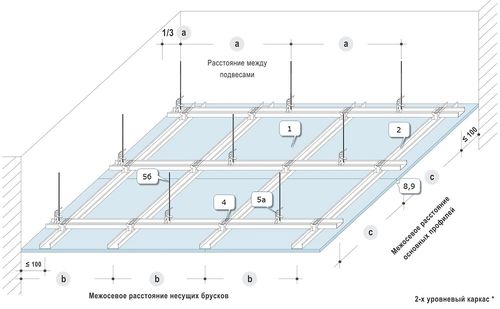
Of all the existing suspended ceiling structures, Armstrong-type ceilings are most often used for finishing large-area non-residential premises.
Suspended ceiling structures Armstrong
Popularity of this suspension system due to the following advantages:
- ease of installation;
- the ability to quickly replace worn-out elements;
- installation of this type of suspended ceiling in rooms with a large area is economically beneficial.
Armstrong ceiling is assembled from metal profile and is a lattice of identical cells measuring 60*60 cm. Next, a tile block made of mineral fiber is placed in each cell. Modular luminaires are produced especially for such suspended ceiling structures. standard sizes. Armstrong modular ceiling lamps are a lighting device made of a metal body and light sources located inside. Depending on the type and purpose of the luminaire, the lamps may be covered protective screen, raster mirror reflective grille, transparent or matte diffuser. Lamps with an open mirror grille create bright lighting necessary for a comfortable working environment in office premises, educational institutions, administrative institutions. Closed lamps with plastic diffusers are suitable for kindergartens, hospitals, clinics.
Specialized industrial modular luminaires have a higher degree of protection against high humidity, dust and exposure to aggressive chemical compounds.
Diversity constructive solutions allows you to successfully use Armstrong ceiling lamps in public buildings, office premises, warehouses, and production workshops.
Armstrong lamps in an office space
Advantages and Disadvantages
Lamps for suspended ceilings Armstrong have both advantages and certain disadvantages. The advantages of modular luminaires include ease of installation, free access to wiring and fastenings, the ability to replace damaged elements without the need to dismantle the structure, and a high level of lighting efficiency. Ceiling lamps, thanks to the fluorescent or LED lamps included in the design, can significantly save on electricity. Another important advantage of the model design is the fact that, if necessary, any tiled block can be easily replaced with a lamp or vice versa. This allows for optimal distribution lighting fixtures. If necessary, you can make the lighting in the room uniform or divide it into zones with different luminous flux intensities.
The disadvantages of these lighting devices include the standard appearance, which is not particularly diverse, if exposed for a sufficiently long time, the “cold” color spectrum of lighting can be tiring; after several years of operation, the brightness of the lighting begins to gradually decrease, and to increase it, replacement of lighting elements is required.
Types of Armstrong lamps

Types of Armstrong lamps
More traditional models are modular designs with fluorescent light sources. A standard luminaire usually uses 4 lamps. Most often, T5 brand bulbs with a power of 14 W or more powerful T8 with 18 W are installed. A feature of lighting devices with fluorescent light sources is the mandatory presence of ballasts. Ballasts can be electromechanical or electronic.
The main disadvantage of electromechanical ballasts is the so-called stroboscopic effect that occurs during startup and operation of the lamp. In other words, an Armstrong ceiling lamp with such a device produces light with high level pulsations. Pulsating light is very tiring for the eyes and is completely unsuitable for rooms in which it is necessary to work with documents, assemble small parts, or perform work that requires constant eye strain. Pulsating lighting significantly reduces labor efficiency and negatively affects the health of workers. Armstrong ceiling lamps with electronic ballasts are practically free of this drawback. In addition, electronic ballasts help extend the service life of modular light sources.
More modern models are ceiling structures with LED lamps. If it is necessary to create simultaneous long-term illumination of a room with a large area, it is better to use LED lamps for Armstrong ceiling.
How to choose the right lamp

Armstrong fluorescent lamp with matte grille
In order to correctly choose the type of lamps for the Armstrong ceiling, it is necessary to compare their main characteristics: energy consumption, brightness and quality of light, service life, price.
Compared to a regular incandescent lamp, fluorescent light bulbs look very attractive because they use five times less electricity. However, comparing the energy consumption of fluorescent and LED light sources, we will see that the latter consume electricity at least two times less. In addition, part of the declared power of fluorescent lighting devices is consumed by ballasts.
Comparing the quality and brightness of the lighting produced different sources, we can come to the conclusion that Armstrong LED ceiling lights are capable of producing brighter and more uniform light. This effect can be partly explained structural device lamps The light from a fluorescent light bulb spreads 360 degrees; a fairly large part of it, despite all sorts of reflective devices, is lost. LEDs are designed in such a way that the flow of light is narrowly directed and limited to a sector the size of a third of a circle. In addition, there is no flicker in LED lamps.
One more important point is the service life of various lighting elements. Average The duration of use of a fluorescent light bulb is about 7 thousand hours. An LED lamp can operate without breakdowns for an average of 40 thousand hours. Even with the most conservative estimates, the service life of an LED light source is several years longer.
The price of fluorescent lighting fixtures is much lower than that of LED lighting fixtures, however, if you take into account the above characteristics, their operation will cost much more.
Safety of operation of ceiling lamps

Armstrong ceiling lamps in the interior
Both LEDs and fluorescent lamps do not overheat and are quite safe from the point of view of fire hazards. Regarding sustainability and compliance sanitary standards, fluorescent light sources are less safe and cause more harm to health: they make noise during operation, ultraviolet radiation negatively affects the skin, and if damaged glass flask light bulbs can release mercury vapor into the air. In this regard, lamps of this type cannot simply be thrown into a trash container; they must be taken to special collection points for subsequent disposal.
Calculation of the number of lamps

Suspended ceiling with Armstrong lamps
Calculation required power the luminous flux should be carried out based on the norms and rules provided for by various regulatory documents. Thus, for lighting public places and work spaces where visual tasks are not performed, 100-150 Lumens per 1 sq.m. is sufficient. m. In office premises, libraries, laboratories, classrooms and auditoriums, lighting should be at least 500 Lumens. In drawing workshops, production premises, in which work is carried out with small details, the luminous flux level should be 1000 Lumens and above. Having determined the power of the required lighting, you can calculate the number of ceiling lighting fixtures. Convert lamp power various types The value of the luminous flux level can be determined based on the following data:
- the power of a fluorescent lamp of 4 W is equal to 120 Lumens, 8 W – 450 Lumens, 15 W – 950 Lumens, 18 – 1350 Lumens;
- led lamp with a power of 4 W, it emits a flux of 400 Lumens, 8 W – 700 Lumens, 10 W – 900 Lumens, 15 W – 1200 Lumens.
Carrying out the calculation required quantity ceiling lighting fixtures, a number of other factors should be taken into account. First of all, the height of the ceilings. Being at different heights from the illuminated surface, the same Armstrong ceiling lamp will be able to provide a luminous flux that is very different in level.
So, if a light source a meter from the surface provides illumination within 1000 Lumens, then, being at a height of 1.5 m, it can provide a luminous flux of only 450 Lumens, and at a distance of 3 m – 115 Lumens.
In addition, when making calculations, it is necessary to take into account the size of the room, the color of the walls, ceiling and floor and their ability to reflect light.
The design characteristics of the lamp itself are also taken into account when calculating. For example, when using a diffuser made of lighting monolithic or embossed polystyrene in the design, the luminous flux transmittance is 85.5%. Matte diffusers have the worst indicator; their luminous flux transmittance is 70%. Prismatic or microprismatic diffusers made of transparent organic glass transmit light best. The transmission coefficient of such a diffuser reaches 90%.
Light has always been one of the most required attributes any comfortable environment. It provides normal conditions for performing all tasks and simply creates comfort. Therefore, it is very important to correctly calculate how many lighting devices are required for a particular room. As a possible example, let's try to calculate lamps for installation in the Armstrong ceiling, used in offices.
Calculation method
The most popular and gives the most optimal numbers now is a method that uses formulas to calculate the amount of light that any of the surfaces in the office receives. This figure is determined based on the reflective ability of all planes - walls, floor and ceiling.
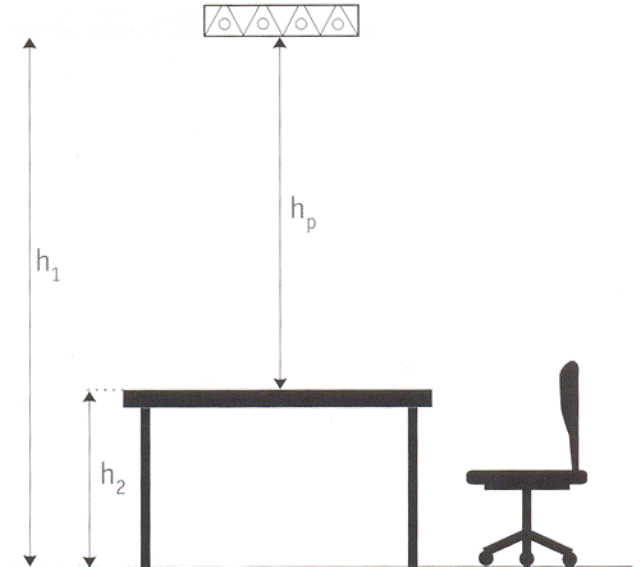
In order to obtain the required value, and with its help the number of lighting devices that will need to be installed, you need to know some overall dimensions and data on the light reflection of all planes. It is also necessary to find out the distance between the ceiling where the illuminator will be mounted and the desktop cover.
Calculation procedure
We will do everything step by step. First, you need to find out the area - multiply the length by the width. With a complex wall configuration, you will have to tinker with calculating this parameter, but it is best if accurate values are used.
S / (h – Kz) * (a + b)
The number of lamps needed is determined by another formula:
(E * S) / (U * n * Fl * Kz)
All Latin numerals mean:
a ,b – length, width
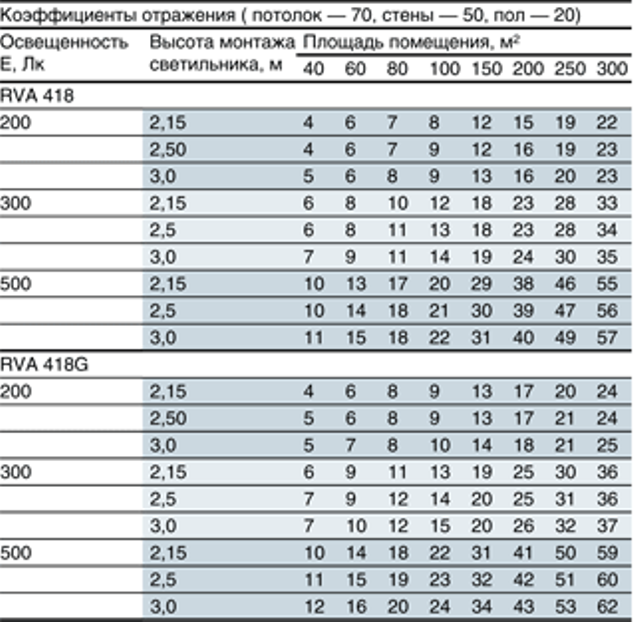
E – the value of the required illumination according to a special table, which is presented below
S – room area
Short circuit - the so-called “safety factor”, which takes into account the natural decrease in the brightness of lamps due to wear or contamination
U – luminous flux utilization indicator
FL – luminous flux produced by one lamp in Lumens
N – number of lamps
h =h 1 – h 2
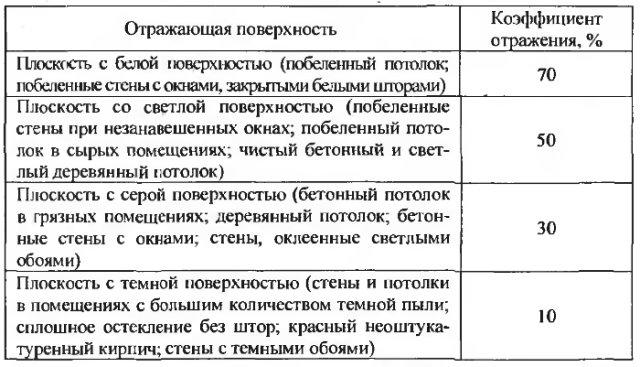
Materials for determining illuminance values
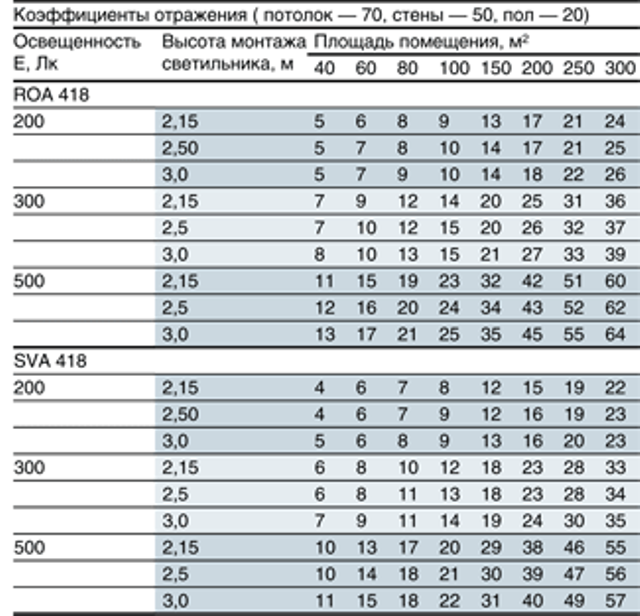
Reflectance coefficients of different surfaces
Calculation example
For example, you can imagine that you need to make a calculation of lamps for the Armstrong ceiling in an office. The side planes of it are presumably light, and the floor covering is gray.
Special devices designed for this type of coating will be installed. They use LEDs with a power of 30 W and a lumen rating of 3250 units. There are 4 diodes in the lamp. The illumination standard for such a room will be 500 lm.
Dimensions office are: ceiling height (h) – 3.2 m, length (a) – 9 m, width (b) – 6 m. At the same time, work surface located at a distance of 0.8 meters from the floor.
The office dimensions will be: 6*9=54 sq. m.
The index according to the formula is calculated as follows: 54 / (3.2-0.8) * (9+6) = 1.5
According to the table, we find the value of luminous flux use: 0.51
(500 * 54) / (0,51 3250 * 0,8) = 20
It turns out that it is necessary to mount 20 devices. The only disadvantage of the method is the rather complicated counting process. In addition, when this method, it is impossible to take into account natural lighting and the configuration of the walls.
Therefore, in a standard situation, the required number of illuminators is considered approximately. For this, the basis is taken that for every five square meters of room area, one lighting device is required. Installation is carried out according to these parameters in almost every second case.





